Child Protection in Addis Ababa (Int’l Day of the African Child)
22 June 2023|Child Protection Project Team, Ethiopia
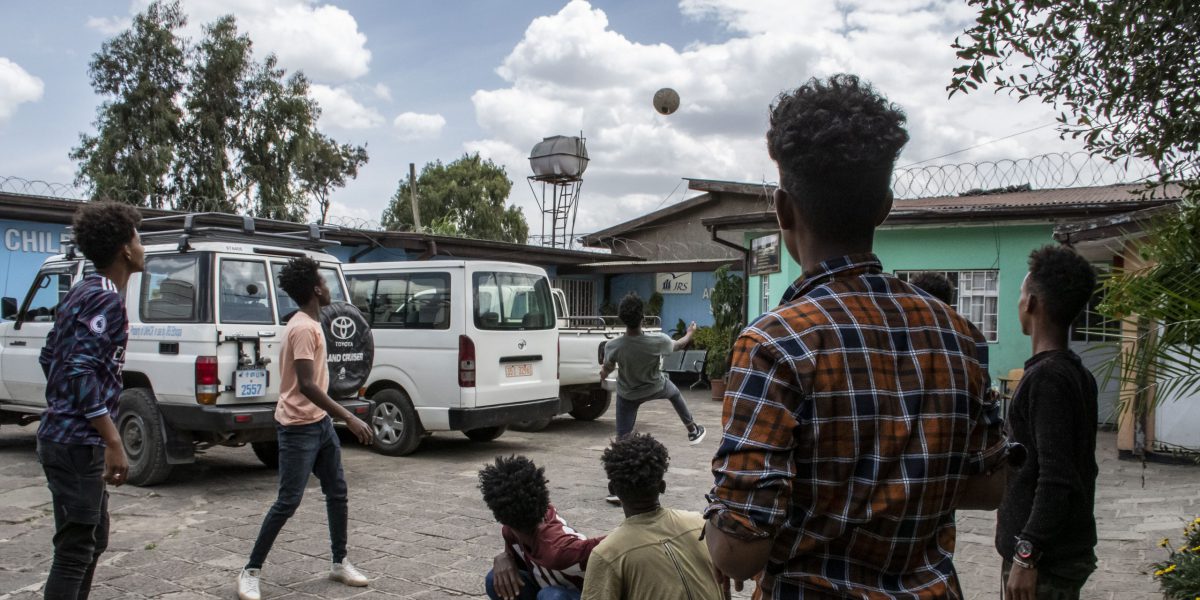
JRS Ethiopia has been implementing a refugee child protection project in Addis Ababa in partnership with UNHCR and Refugee and Returnees Service (RRS) since July 2017 to provide comprehensive

child protection services for unaccompanied and separated and other refugee children at risk living in Addis Ababa. Over the years, the number of refugee children including unaccompanied and separated children has been increasing in the city. The outbreak of war in northern Ethiopia led to an increment of refugee children particularly unaccompanied and separated and other refugee children in the city. By the end of 2022, there were around 77,433 refugees in Addis Ababa. Eritrean refugees represent 92 % of the refugee population in Addis Ababa.
Refugee children account for 30 % of the total refugee in the city. There were 2623 (1294 F,1329M) unaccompanied or separated refugee children. Meanwhile, there were 2,683 (1285F,1398M) refugee children at various risks
(source: UNHCR 2022)1.
This has been increasing the demand for child protection services in urban areas, particularly in Addis Ababa. This has obliged JRS to strengthen and expand its services by opening a new Child Protection (CP) and Mental Health and Psychosocial Support (MHPSS) Center around Ayat Square in Addis Ababa with funding from PRM (August 2022). The goal of the JRS’s child protection program is to provide and strengthen child protection interventions and address the mental health and psychosocial needs of urban refugees focusing on unaccompanied and separated refugee children and other vulnerable children and youth. In line with this, the project’s primary target groups are separated refugee children, caregivers, and refugees in need of various CP and MHPSS services.

The CP program has provided quality case management services by conducting Best Procedures (BIA and BID), facilitating alternative care arrangements for unaccompanied and separated refugee children, and providing monthly cash-based assistance to children who were under foster care arrangement. Besides better parenting skills training, emergency individual protection assistance, non-formal education, life skill training, capacity building training for staff and refugee community structures, awareness raising workshops on SGBV, sexual and reproductive health, and menstrual hygiene management, monthly ROVs and case management member’s meetings, PTA meetings, home visit programs, and monthly child parliament sessions effectively carried out under child protection program. JRS has also increased the number of Child Protection Refugee Outreach Volunteers (ROVs) from 20 to 50 to reach many refugee children residing in Addis Ababa.
 On the other hand, MHPSS services have been carried out through implementing counseling services, availing psychosocial services (recreational, sport, etc.), life skills training, psychoeducation and MHPSS awareness raising, advocacy events, capacity building of community structures on MHPSS, and conducting primary health care unit MHPSS service facility readiness assessments.
On the other hand, MHPSS services have been carried out through implementing counseling services, availing psychosocial services (recreational, sport, etc.), life skills training, psychoeducation and MHPSS awareness raising, advocacy events, capacity building of community structures on MHPSS, and conducting primary health care unit MHPSS service facility readiness assessments.
To ensure community participation and effective implementation of the CP and MHPSS activities, different community structures organized and conducted regular follow-up and monitoring programs; event days were also held to accompany beneficiaries. These events provided an opportunity for beneficiaries to share their experiences. They helped further foster trust and understanding between the community and humanitarian actors and ensure safe and effective assistance delivery. Additionally, the structures enable the community to become more involved in development and decision-making.
1 Document – UNHCR Ethiopia Statistics Urban refugees Addis Ababa November 2022 https://data.unhcr.org/en/documents/details/97679


